Moroccan orange exports continued to expand for a second season in a row, gradually recovering after the sharp decline recorded in 2022/23, according to EastFruit.
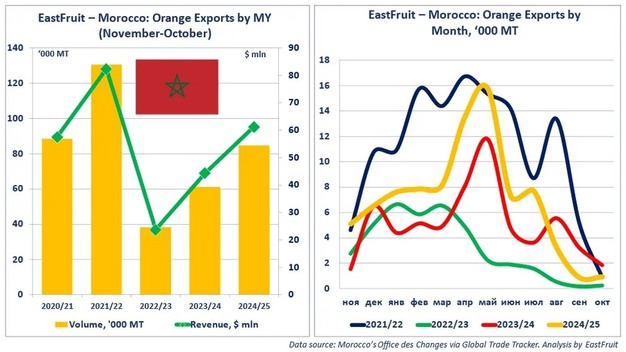
In the 2024/25 season from November to October, Morocco exported 84.6 thousand tons of oranges with a value of US$61 million. Export volumes were 38 per cent higher than in the previous season and more than double the low point reached in 2022/23.
Oranges remain one of Morocco's core fruit export categories. During the first 10 months of 2025, orange exports ranked behind mandarins, watermelons, and blueberries. The Moroccan orange export campaign starts in November and reaches its seasonal high in spring, driven by the Maroc Late variety. In the 2024/25 season, the highest monthly export volume was recorded in May, at 15.7 thousand tons.
 © EastFruit
© EastFruit
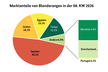
Canada and the United States remained the main destinations for Moroccan oranges, accounting for 22.0 per cent and 21.5 per cent of total shipments, respectively. Exports to Canada increased by 65 per cent compared with the previous season, while volumes to the United States declined, making it the only country among Morocco's top ten destinations to record a reduction. Russia ranked third and continued to increase imports of Moroccan produce amid European sanctions.
Shipments to the United Kingdom increased sevenfold, exports to Saudi Arabia rose fivefold, and volumes shipped to Spain tripled. Exports to Portugal resumed, while sales to the Netherlands, France, Mauritania, and Senegal also increased. In total, Moroccan oranges were shipped to 46 countries during the 2024/25 season.
 © EastFruit
© EastFruit
Despite the recent expansion, Moroccan orange exports continue to face structural constraints. Climate change and ongoing water shortages have increased the frequency and severity of droughts, affecting production and export availability. The highest export volume was recorded in the 2016/17 season, when 164 thousand tons were shipped. Volumes declined almost every year thereafter, reaching a low in 2022/23.
Since 2024, the Moroccan government has subsidized citrus exports to Europe, supporting price competitiveness against Egyptian supply during certain months.
Export performance over the past two seasons indicates a gradual recovery. Although volumes remain below earlier highs, shipment data suggest that Morocco is partially offsetting recent production and market challenges through expanded market reach.
Source: EastFruit