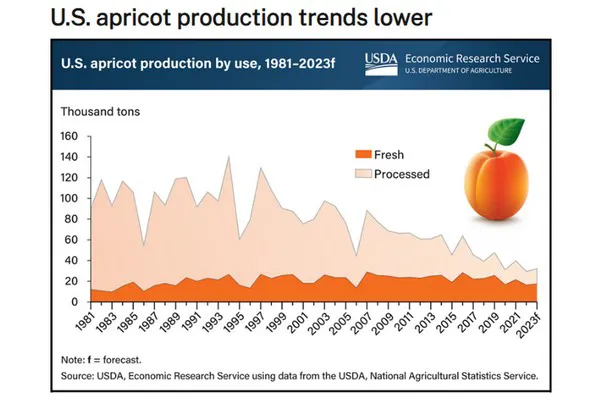
Apricots, a stone fruit like peaches, plums, and nectarines, are typically either processed by canning, freezing, or drying, or sold as fresh, whole apricots. Regardless of how you like apricots, their production has been decreasing since the 1990s in response to falling US consumption, especially for processed apricots.
Commercial production is concentrated on the West Coast, with California representing 90 percent of apricot production in 2023. The US apricot industry has experienced a long-term downward trend in bearing acreage, falling 62 percent over the past 20 years. Growing competition from imports of processed apricot products and a general increase in consumption for all fresh fruit have encouraged growers to divert more of their acreage to higher valued commodities, resulting in fewer bearing acres of apricots and shifts in use.
The downward trend in production has coincided with a decrease in the share of apricots used in the processing market. During the first three seasons of this decade (2020–22), processed utilization has averaged 45 percent—down from 63 percent during the early 2010s and 89 percent in the early 1980s. This reflected both small gains in fresh market use and a marked downward trend in processing uses (particularly canned and frozen). Until the 2020s, the volume used as fresh apricots had been trending higher each decade—roughly pacing population growth.
Source: ers.usda.gov