The start of the new season for European apples shows a decrease of one percent in the total production. The market has clearly split in two parts in terms of price levels. The market for fresh apples is better than last year, while the market for the industry apples collapsed.
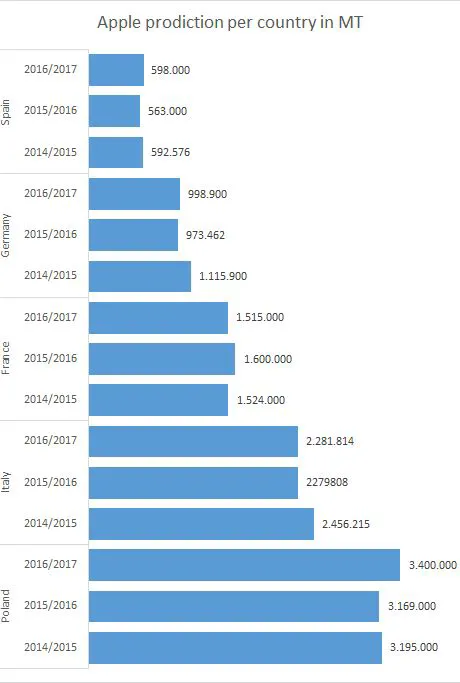
The total production in Europe is 11.3 million tons, which is a drop of 2 percent relative to the previous year. This total volume actually hides the developments in several Member States. Poland is the only one who has positive numbers, because in large parts of Central and Eastern Europe, the harvest has been decimated due to a late frost period. Snow and frost in April reduced the harvest in Slovenia, Austria, Slovakia, Croatia, Czech Republic, and Hungary. In Austria, the harvest was hit hardest, the production decreased with 82 percent.

Romanian law
The damage in other countries ranged from 8 to 78 percent of the harvest. For neighbouring countries, this situation creates opportunities for increasing the export to these countries. Besides Poland, there are more countries that have high volumes. Germany, Spain, Romania, Greece, and the United Kingdom found that their harvest was larger than expected. In several countries, this resulted from new plantations that came into production. This applies to Poland, amongst others. In other countries, such as Germany, Spain, and Romania, the harvest recovered after a bad preceding season.
The European Union is one of the market leaders in terms of apple production. Within the EU, there are 5 countries that together count for 77 percent of the production. The five countries are Poland (30%), Italy (20%), France (13%), Germany (9%), and Spain (5%). The Spanish apple acreage is slowly decreasing. The producers are removing apple trees to plant stone fruit trees. Romania can improve its position on the list, however. The government has adopted a proposal that states that retailers have to get at least 51 percent of their fruit from a ‘short supply chain’, from January 2017. This could stimulate the national fruit production.
New varieties
There are about 25 varieties that are produced on commercial basis in Europe. These varieties generate together more than 10,000 tons. Amongst which there are the Golden Delicious, Royal Gala, and Idared that are produced the most. The pattern differs per member state. The Golden Delicious might be the largest in Italy, France, and Spain, in the Netherlands and Germany, it is the Elstar that tops all. The Idared is the largest in Poland and Hungary, however. The Gala, which is in the top three of most produced varieties, is in none of the member states the largest. Newer varieties, such as the Pink Lady, Kanzi, Rubens, Tentation, and Kiku, their market shares are increasing. In the Netherlands, these varieties have a market share of 10%.
Besides the commercial production, there is a part of non-commercial production. Not all member cities have numbers about this cultivation, but from the available date, it seems that this production is growing as well, especially in Germany and Hungary. Overall, a growth of 16 percent is calculated, which is equivalent to 1.24 million ton apples. This is more than enough to compensate the losses in Austria, Slovenia, and the Czech Republic.
Import through the Netherlands and UK
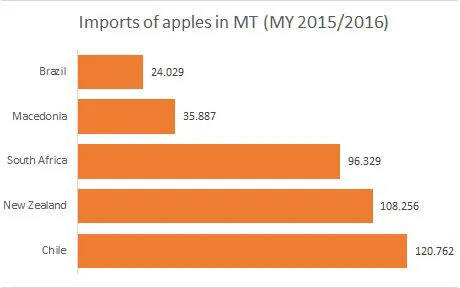
The major part of the apples stays within European borders. During the past five years, an average of 2.2 million ton apples is traded between member states. In contrast is the import of 400,000 to 800,000 ton from outside the EU. This is equivalent to 3 to 6 percent of the total volume. It is expected that the severely decreased harvest in the Eastern European countries means an increase in import from neighbouring countries.
There are three countries that account for 70 percent of the supply in terms of import. These countries can all be found on the southern hemisphere and the trade flow is especially visible outside the European season. The United Kingdom and the Netherlands account for 58% of this import together. The Netherlands functions as a transit port for apples to the European hinterland; the major part is exported.
Closed borders Russia
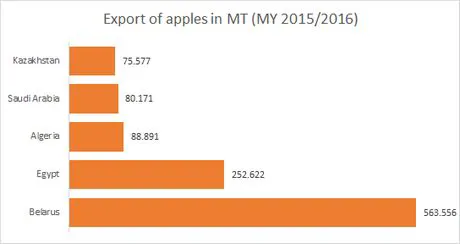
The export of European apples will slightly increase this year. Because of the closed borders of Russia, the surrounding member states have started looking for different markets in Eastern Europe, Northern Africa, the Middle East, and Brazil. There, the countries had varying success. The most successful was the export of the Gala, Granny Smith, Golden Delicious, and Red Delicious. Besides, countries that were used to working with new markets before the boycott was proclaimed are more successful in opening new markets. The most important export markets in 2015/2016 were Belarus, Egypt, and Algeria. The largest exporters account together for 90% of the European export, and they are Poland, Italy, France, Latvia, and Greece.
Normally, the EU has no arrangements to take a product from the market, but as a result of the Russian boycott, the EU implemented an intervention measure in 2014. In that first year, more than 14 million ton apples were taken from the market. This volume has decreased since then. Between July 2015 and 2016, 100,000 ton apples were taken from the market.








